Generate carbon dioxide from a chemical reaction and perform the limewater test to show the mix of gases
This experiment provides evidence that particles in a gas are in motion.
This experiment should take 30 minutes.
Equipment
Apparatus
- Eye protection
- Test tubes, x3
- Cork
- Delivery tube and bung
Chemicals
- Limewater 0.02 mol dm–3
- Calcium carbonate
- Hydrochloric acid 0.5 mol dm–3
Health, safety and technical notes
- Read our standard health and safety guidance.
- Wear eye protection, if desired.
- Hydrochloric acid is an eye irritant, see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC057
Procedure
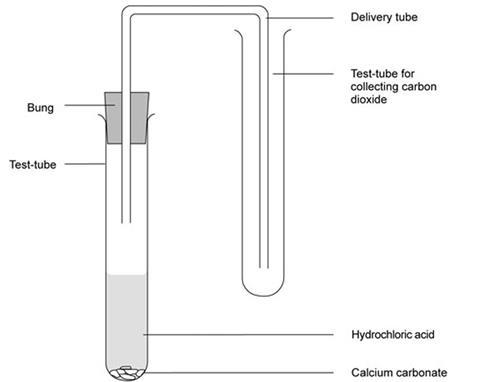
- Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
- Put a spatula measure of calcium carbonate into the first test-tube.
- Add 10 cm3 of hydrochloric acid and quickly replace the bung and delivery tube. Ensure the delivery tube reaches almost to the bottom of the second test-tube.
- Allow the gas to pass into the second test-tube for about one minute, then remove the delivery tube and cork the test-tube.
- Hold the test-tube upside down over a similar test-tube containing air.
- Remove the cork and place the tubes mouth-to-mouth.
- After 5 min, cork both tubes and test the contents for carbon dioxide (swirl a little limewater round in the test-tube). Write down what happens in both tubes.
- Repeat this experiment but this time at step 5 hold the test-tube of air upside down over a test-tube of carbon dioxide.
Notes
This experiment provides a good introduction, one suggestion is to show a demonstration of Brownian motion using a smoke cell after this experiment
Solids, liquids and gases consist of minute particles. If this were not the case, they would not mix so easily.
This is not proof of a particulate theory, but the experiment does suggest that the particles in the gas must be in motion to spread through the air in the containers.
Questions
- Which of the four test-tubes contained carbon dioxide at the end of the experiment?
- Is air or carbon dioxide more dense?
- Does this experiment support the idea that the particles of a gas are in motion? Give your reasons
Answers
- All the test-tubes contained carbon dioxide; the gases always diffuse and mix.
- Carbon dioxide is denser than air.
- Yes; both tubes should give cloudy limewater, suggesting the gases in the two tubes mixed. Some of the heavier carbon dioxide molecules moved upwards into the test-tube containing air.
Downloads
Particles in motion - student sheet
PDF, Size 0.16 mbParticles in motion - teacher notes
PDF, Size 0.12 mb
Additional information
This practical is part of our Classic chemistry experiments collection.


















No comments yet