- Home
- I am a …
- Resources
- Collections
- Post-lockdown teaching support
- Remote teaching support
- Starters for ten
- Screen experiments
- Assessment for learning
- Microscale chemistry
- Faces of chemistry
- Classic chemistry experiments
- Nuffield practical collection
- Anecdotes for chemistry teachers
- More …
- Literacy in science teaching
- Climate change and sustainability
- Alchemy
- On this day in chemistry
- Global experiments
- PhET interactive simulations
- Chemistry vignettes
- Context and problem based learning
- Journal of the month
- Chemistry and art
- Classic chemistry demonstrations
- In search of solutions
- In search of more solutions
- Creative problem-solving in chemistry
- Solar spark
- Chemistry for non-specialists
- Health and safety in higher education
- Analytical chemistry introductions
- Exhibition chemistry
- Introductory maths for higher education
- Commercial skills for chemists
- Kitchen chemistry
- Journals how to guides
- Chemistry in health
- Chemistry in sport
- Chemistry in your cupboard
- Chocolate chemistry
- Adnoddau addysgu cemeg Cymraeg
- The chemistry of fireworks
- Festive chemistry
- Collections
- Education in Chemistry
- Teach Chemistry
- Events
- Teacher PD
- Enrichment
- Our work
- More from navigation items
Close menu
- Home
- I am a …
-
Resources
- Back to parent navigation item
- Resources
- Primary
- Secondary
- Higher education
- Curriculum support
- Practical
- Analysis
- Literacy in science teaching
- Periodic table
- Climate change and sustainability
- Careers
- Resources shop
-
Collections
- Back to parent navigation item
- Collections
- Post-lockdown teaching support
- Remote teaching support
- Starters for ten
- Screen experiments
- Assessment for learning
- Microscale chemistry
- Faces of chemistry
- Classic chemistry experiments
- Nuffield practical collection
- Anecdotes for chemistry teachers
- More …
- Literacy in science teaching
- Climate change and sustainability
- Alchemy
- On this day in chemistry
- Global experiments
- PhET interactive simulations
- Chemistry vignettes
- Context and problem based learning
- Journal of the month
-
Chemistry and art
- Back to parent navigation item
- Chemistry and art
- Techniques
- Art analysis
- Pigments and colours
- Ancient art: today's technology
- Psychology and art theory
- Art and archaeology
- Artists as chemists
- The physics of restoration and conservation
- Cave art
- Ancient Egyptian art
- Ancient Greek art
- Ancient Roman art
- Classic chemistry demonstrations
- In search of solutions
- In search of more solutions
- Creative problem-solving in chemistry
- Solar spark
- Chemistry for non-specialists
- Health and safety in higher education
- Analytical chemistry introductions
- Exhibition chemistry
- Introductory maths for higher education
- Commercial skills for chemists
- Kitchen chemistry
- Journals how to guides
- Chemistry in health
- Chemistry in sport
- Chemistry in your cupboard
- Chocolate chemistry
- Adnoddau addysgu cemeg Cymraeg
- The chemistry of fireworks
- Festive chemistry
- Education in Chemistry
- Teach Chemistry
- Events
- Teacher PD
- Enrichment
- Our work
Pigments and colours
Inventing new colours for art has taxed the finest scientists and using them has inspired the finest artists. Find out how some of the strangest ingredients bring colour to art.
Practical resources
Making a crystal garden
In association with Nuffield Foundation
Create chemical gardens with your students by growing crystals of coloured silicates in this class practical. Includes kit list and safety instructions.
Spinning colour top
In this experiment, students observe, describe and explain what happens when a multicoloured disc spins at a high speed.
Flame tests using metal salts
In this classic science experiment, students report on the colours produced when flame tests are carried out on different metal salts.
Tyndall effect- why the sky is blue
In this experiment, students observe and report on the Tyndall effect. Also, students use their knowledge of the properties of mixtures and emulsions, and light to explain their observations.
Ancient inks
In this practical, students use methods which have been used for centuries to produce inks.
Making brown ink
This practical is suitable for all pupils as part of a general introduction to coloured substances.
Making paint with minerals
This practical is best done with groups of four pupils each pupil could chose a single mineral and make both tempera paint and an oil paint for testing.
Making and using blueprint paper
Blueprints use the cyanotype process invented by the astronomer John Herschel in 1842. In this experiment you will carry out an experiment to produce blueprint paper and produce an image or diagram using the blueprint paper.
Making a simple paint
In this practical, students use a process which has been used for centuries to produce egg tempera paint.
All resources
The emergence of new techniques and pigments
The emergence of new techniques and pigments within Greek art
Roman glass and its chemistry
Roman glass is found all over the Roman Empire, but how different is it?
Prehistoric pigments
What pigments were used for cave painting and where did they come from?
Roman commerce in pigments
Did the Romans use the same materials as the Greeks in their painting? And where did the pigments come from?
Were Ancient Greek statues white or coloured?
Renaissance artists studied the sculptures and monuments of Greece and Rome and emulated them in their own work, ie they imitated the art. This perspective of art has echoed down the centuries to influence the appearance of Western art and architecture today.
Three colours from the same dye-bath
In this experiment, students see if dyes bond differently depending on the material, and what effect this has.
Greek art theory influences future art
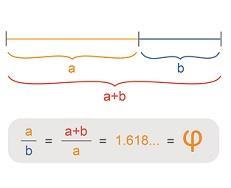
Here we look at how the influences on Ancient Greek art, including the importance, and what is meant by, the Goldern Ratio.
Egyptian blue
The Egyptians sought a permanent blue pigment to depict their royalty and gods with the necessary reverence. Here we look at how the Egyptian achieved a blue pigment that didn’t degrade over time.
Egyptian myths
The Egyptians developed a world view in which events and conditions were attributed to the actions of multiple, related gods and goddesses. Here are some of those stories.
Egyptian materials and pigments
Ancient Egyptian artists are known for developing a wider range of materials for their art.This resource looks at the pigments and materials the Egyptians used to create their art.
Egyptian art
To understand and appreciate Egyptian art one must look at the beginnings of art in Egypt and how it developed, for in that development lay the roots of many ideas and techniques. This resources explores this development.